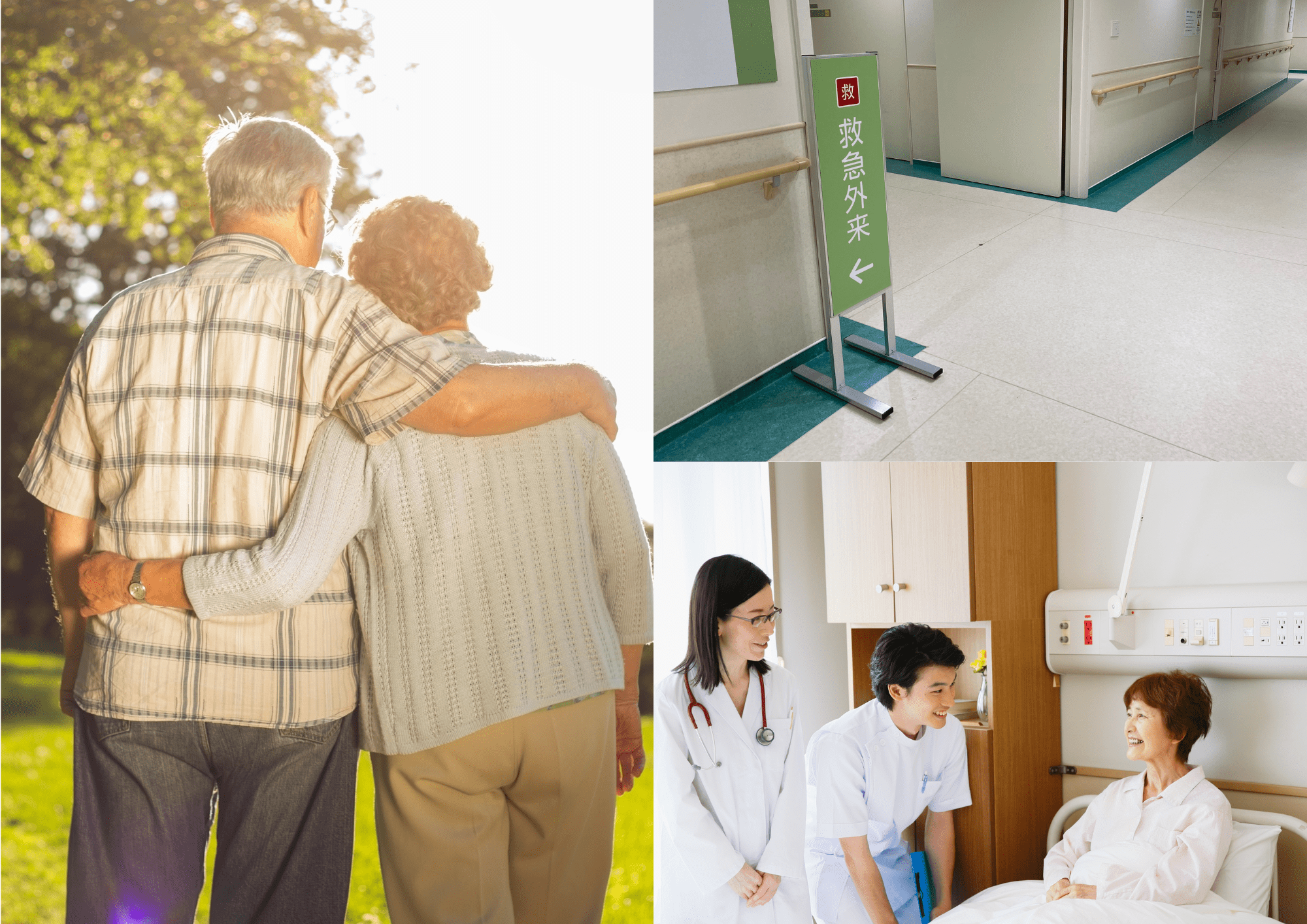
Health in Japan is a global concern due to its high life expectancy and effective healthcare system. Factors contributing to the health and longevity of Japanese people, such as a healthy diet, an active lifestyle, social support, and easy access to healthcare services, contribute to this achievement. Furthermore, Japan has a culture that values physical and mental health, and has ancient healthcare traditions that are still practiced today. These factors contribute to Japan's position as one of the countries with a high life expectancy.
There are several aspects of Japan's healthcare system:
- Compulsory Health Insurance:
Japan implements a universal health insurance system that requires all citizens and residents to have health insurance
There are two types of mandatory insurance: employment-based plans and residence-based plans.
- Easy Access to Healthcare:
Japanese people have easy access to various healthcare facilities, including hospitals and clinics.
Japan has a universal health insurance system that requires all citizens and residents to have insurance, whether from the government or private sector. This ensures that everyone has access to healthcare regardless of socioeconomic status.
There is an extensive network of hospitals and clinics throughout the country, in both urban and rural areas. This makes it easy for people to get the medical care they need, whether in public or private facilities.
Japan's health insurance system helps keep healthcare costs affordable for everyone, even those with low incomes or the elderly
Japanese healthcare facilities, both hospitals and clinics, are known for their high standards of service and use of advanced medical technology
- Improved Healthcare
Japan is continuously striving to improve the quality of healthcare services, including medical education and community-based care.
There are also several factors contributing to health in Japan
- Healthy Diet
Japanese people are known for their diet rich in fresh foods such as fish, vegetables, and fermented foods, which contribute to digestive health and longevity
- Active Lifestyle
Japan has a culture that encourages an active lifestyle, including walking, sports, and other physical activities
This is supported by a variety of factors, including good public transportation policies, pedestrian-friendly city design, and a culture that values health and fitness
- Social Connection
Japanese society has strong social bonds, which support mental and emotional well-being.
Many Japanese people are involved in various community activities, such as hobby groups, village events, or volunteering. This allows them to build strong social relationships and feel connected to others
For example, in Okinawa, there is the tradition of moai, social circles that provide financial and emotional support. Moai members support each other in various situations, creating a sense of community and security
Japanese society has a strong etiquette of social interaction, such as bowing (ojigi), greetings, and maintaining good manners. This helps create a harmonious and respectful social environment.
- Ancient Health Traditions:
Traditions such as onsen (natural hot springs), shinrin-yoku (forest therapy), and Zen practices, such as meditation and yoga, also contribute to physical and mental health.
Challenges and Innovations
- Aging Demographics:
Japan faces challenges due to its aging population, which requires changes in its healthcare system.
Japan faces significant challenges due to its aging population, which demands significant changes in its healthcare system. The increasing number of elderly people, coupled with a declining birth rate, is placing significant pressure on the healthcare system, including hospitals, long-term care services, and home care
- Climate Change
Climate change in Japan is also a concern, with health impacts such as heat-related illnesses and natural disasters particularly affecting public health. Rising temperatures and extreme weather, such as heat waves, can increase the risk of heat-related illnesses like heatstroke, and natural disasters like floods can also impact health
- Innovation in Medical Education
Japan is undertaking reforms in medical education to meet the needs of an aging society and changing healthcare needs
Japan is responding to the challenges of an aging population and changing healthcare needs by adapting the curriculum, focusing on community-oriented care, and developing a care system more suited to its aging population
Conclusion:
Health in Japan is the result of a combination of an effective healthcare system, a culture that supports healthy lifestyles, and a rich healthcare tradition. By continuously innovating and adapting to new challenges, Japan strives to maintain and improve the health of its people.
Data source: Rhike Resty A, S.S